4.2 定量评估 Quantitative Evaluation
We evaluate LSD-SLAM on the publicly available RGB-D dataset [25].
我们通过现有RGB-D公开的数据集[25]来评估LSD-SLAM算法。
Note that for monocular SLAM this is a very challenging benchmark, as it contains fast rotational movement, strong motion blur and rolling shutter artifacts.
值得注意的是,这个benchmark对单目SLAM来说很有挑战性,因为数据集里面包含相机的快速旋转运动,强烈的动态模糊(或运动模糊motion blur)和滚动快门伪影效果(rolling shutter artifacts)等难点。
We use the very first depth map to bootstrap the system and get the correct initial scale.
我们通过最早的一帧关键帧上的深度图(初始化),来启动整个LSD-SLAM系统,并获得正确的初始场景尺度。
Table 9 shows the resulting absolute trajectory error, and compares it to other approaches.
图表9罗列的是(相机)绝对轨迹的标准误差,并和其他SLAM算法比较精度的实验结果。
改动_Labby: absolute trajectory error建议翻译为:轨迹的绝对误差
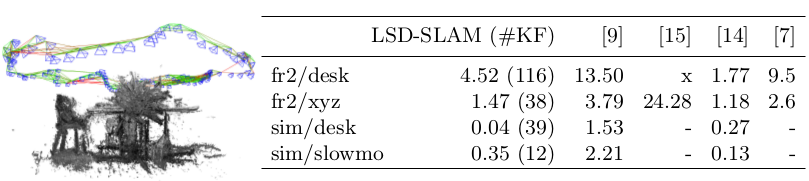
image copy right belongs to engel14eccv paper, 图像摘录自 engel14eccv论文
Fig. 9: Results on the TUM RGB-D benchmark [25], and two simulated sequences from [12], measured as absolute trajectory RMSE (cm).
图示9:运行在TUM RGB-D 数据集 benchmark [25]上的结果,还包括两个[12]仿真图像序列集(的实验),测量(计算出来的)绝对轨迹的标准误差(或叫均方根误差 RMSE)(厘米 cm)
(左图显示的是TUM fr2/desk图像序列,译者额外添加备注)
For LSD-SLAM, we also show the number of keyframes created. ’x’ denotes tracking failure, ’-’ no avail- able data.
图表中,我们在LSD-SLAM这一列还标注了关键帧的数量,’x’ 表示图像跟踪失败,’-’ 没有可用的数据(造成的原因?需要确认,译者额外添加备注)。
For comparison we show respective results from semi-dense mono-VO[9], keypoint-based mono-SLAM [15], direct RGB-D SLAM [14] and keypoint-based RGB-D SLAM [7].
我们还使用其他四种算法来和LSD-SLAM算法比较,它们是:
- semi-dense mono-VO [9]
- keypoint-based mono SLAM [15]
- direct RGB-D SLAM [14]
- keypoint- based RGB-D SLAM [7]
Note that [14] and [7] use depth information from the sensor, while the others do not.
注意的是, [14] 和[7]使用RGB-D相机的深度信息,其他算法都是单目。