审稿中...
1. Introduction 引言
1.1 paragraph
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) has been a hot research topic in the last two decades in the Computer Vision and Robotics communities, and has recently attracted the attention of high-technological companies.
SLAM(同时定位与地图重建)在过去的20年中,一直是计算机视觉和机器人领域的热门话题,同时也吸引了很多高科技公司的关注。
SLAM techniques build a map of an unknown environment and localize the sensor in the map with a strong focus on real-time operation.
SLAM技术是在未知的环境当中建立一个地图并且能够在地图当中实时的定位。
Among the different sensor modalities, cameras are cheap and provide rich information of the environment that allows for robust and accurate place recognition.
在不同类型的传感器当中,相机十分廉价,并且能够提供丰富的环境信息,受到研究者的青睐。相机提供的图像信息可以用作鲁棒的和精确的位置识别。
Place recognition is a key module of a SLAM system to close loops (i.e. detect when the sensor returns to a mapped area and correct the accumulated error in exploration) and to relocalize the camera after a tracking failure, due to occlusion or aggressive motion, or at system reinitialization.
位置识别是SLAM系统中回环检测的关键模块(例如,当传感器检测到一个已经建好图的位置的时候,可以进行修正在探索过程中的误差)以及,能够修正由于剧烈的震动或者在系统进行初始化的时候在相机跟踪失败后的重新定位。
Therefore Visual SLAM, where the main sensor is a camera, has been strongly developed in the last years.
因此以相机为核心的视觉SLAM在过去的一年中得到快速的发展。
1.2 paragraph
Visual SLAM can be performed by using just a monocular camera, which is the cheapest and smallest sensor setup.
视觉SLAM仅仅通过一个单目相机就能够完成。单目相机也是最便宜也是最小巧的传感器设备。
However as depth is not observable from just one camera, the scale of the map and estimated trajectory is unknown.
然而深度信息无法从单目相机中观测到,地图的尺度和预测轨迹是未知的。
In addition the system bootstrapping require multi-view or filtering techniques to produce an initial map as it cannot be triangulated from the very first frame.
此外,由于不能从第一帧当中进行三角测量化,单目视觉SLAM系统的启动往往需要多个视角或者滤波技术才能产生一个初始化的地图。
Last but not least, monocular SLAM suffers from scale drift and may fail if performing pure rotations in exploration.
最后,单目SLAM可能会造成尺度漂移,以及在探索的过程中执行纯旋转的时候可能会失败。
By using a stereo or an RGB-D camera all these issues are solved and allows for the most reliable Visual SLAM solutions.
通过使用一个双目或者RGB-D相机将会解决这些问题,并且能够成为一种更加有效的视觉SLAM的解决方案。
1.3 paragraph
In this paper we built on our monocular ORB-SLAM [1] and propose ORB-SLAM2 with the following contributions:
在这篇文章当中,我们在单目ORB-SLAM[1]的基础上提出ORB-SLAM2,有以下贡献:
first open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras, including loop closing, relocalization and map reuse.
这是首个基于单目,双目和RGB-D相机的开源SLAM方案,这个方案包括,回环检测,地图重用和重定位。
Our RGB-D results shows that by using Bundle Adjustment (BA) we achieve more accuracy than state-of-the-art methods based on ICP or photometric and depth error minimization.
我们的RGB-D结果说明,光速法平差优化(BA)比ICP或者光度和深度误差最小方法的更加精确。
By using close and far stereo points and monocular observations our stereo results are more accurate than the state-of-the-art direct stereo SLAM.
通过匹配远处和近处的双目匹配的点和单目观测,我们的双目的结果比直接使用双目系统更加精确。
A lightweight localization mode that can effectively reuse the map with mapping disabled.
针对无法建图的情况,提出了一个轻量级的定位模式,能够更加有效的重用地图。
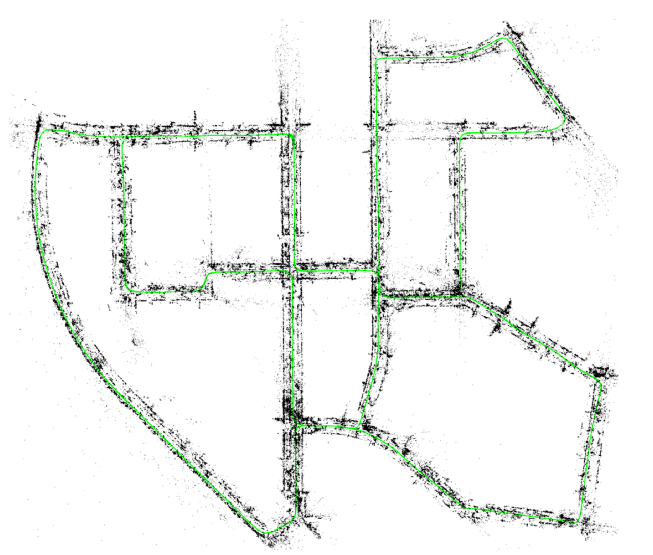
image copy right belongs to Raúl Mur-Artal and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475
图像摘录自ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475
(a) Stereo input: trajectory and sparse reconstruction of an urban environment with multiple loop closures.
(a)双目输入:带有多次回环检测的城市环境轨迹和稀疏重建。
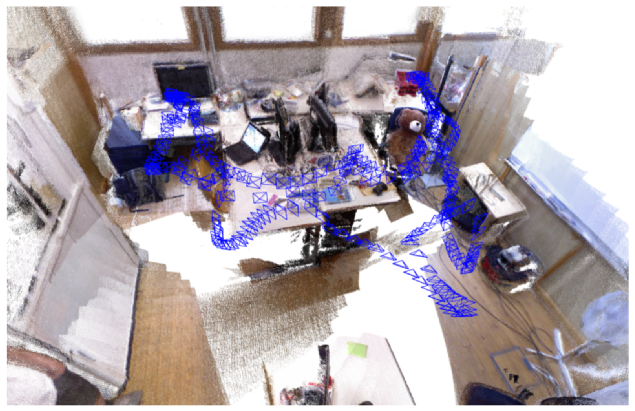
image copy right belongs to Raúl Mur-Artal and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475
图像摘录自ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475
(b) RGB-D input: keyframes and dense pointcloud of a room scene with one loop closure. The pointcloud is rendered by backprojecting the sensor depth maps from estimated keyframe poses. No fusion is performed.
(b) RGB-D输入:房间关键帧和稠密点云已经一次回环检测图,这些点云通过对深度图的关键帧的位姿进行映射得到。不进行渲染(融合?)。
Fig. 1. ORB-SLAM2 processes stereo and RGB-D inputs to estimate camera trajectory and build a map of the environment. The system is able to close loops, relocalize, and reuse its map in real-time in standard CPUs with high accuracy and robustness.
图1 是ORB-SLAM2处理双目和RGB-D输入评估相机的轨迹并建图。这个系统能够保证在高精度和鲁棒性的前提下,做到在标准CPU上进行实时的,回环检测,重定位以及地图重用。
1.4 paragraph
Fig. 1 shows examples of ORB-SLAM2 output from stereo and RGB-D inputs.
图a中显示的是双目和RGB输入下的ORBSLAM2的输出。
The stereo case shows the final trajectory and sparse reconstruction of the sequence 00 from the KITTI dataset [2].
双目例子显示的是最后轨迹和稀疏重建的地图。这里的数据集来源于KITTI的Sequence00数据集。
This is an urban sequence with multiple loop closures that ORB-SLAM2 was able to successfully detect.
这个城市数据集是ORB-SLAM2多次成功提取特征,并且回环检测而来。
The RGB-D case shows the keyframe poses estimated in sequence fr1 room from the TUM RGB-D Dataset [3], and a dense pointcloud, rendered by backprojecting sensor depth maps from the estimated keyframe poses.
RGB-D例子是来源于TUM 的RGB-D 数据库中的fr1_room的数据集,并且进行关键帧的位姿评估而来。通过评估关键帧的位姿,映射深度图,最终形成一个稠密的点云图。
Note that our SLAM does not perform any fusion like KinectFusion [4] or similar, but the good definition indicates the accuracy of the keyframe poses.
值得注意的一点是,ORB-SLAM2虽不像Kinect Fusion一样进行数据融合,但是却能够很精确的估计关键帧的位姿。
More examples are shown on the attached video .
更多的例子在附件视频中展示。
In the rest of the paper, we discuss related work in Section II, we describe our system in Section III, then present the evaluation results in Section IV and end with conclusions in Section V.
在余下的篇章当中,我们将会在第二部分讨论相关的工作。在第三部分谈论ORB-SLAM2系统框架。第四部分评价ORB-SLAM2,第五部分得出结论。